On this page
China's railway transportation system is one of the most developed and extensive in the world, with over 140,000 kilometers of rail lines, including approximately 38,000 kilometers of high-speed rail (HSR) lines. The railway network connects major cities and tourist attractions across the country and is especially crucial during holidays, as it effectively manages the massive flow of people, ensuring safe travel.
Types of Trains
In the Chinese railway system, trains starting with different letters represent different train series. Here is a brief introduction to each:
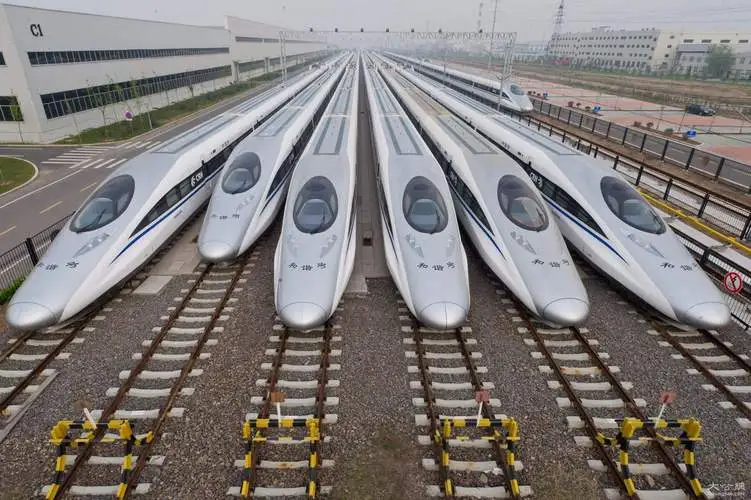
- G-series trains
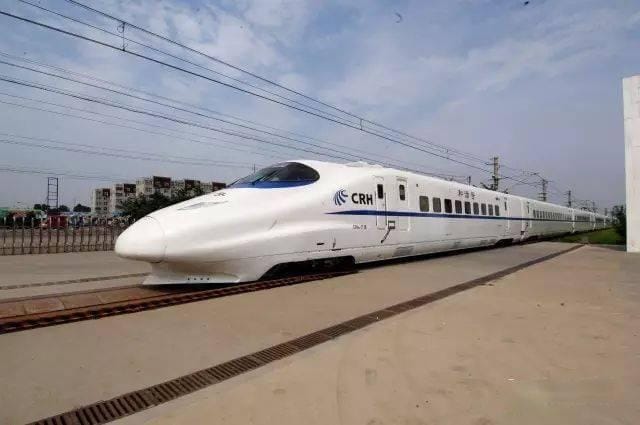
G stands for "Gao Su" (high speed), which refers to China's high-speed trains. These trains operate on high-speed rail lines and can reach speeds of up to 350 kilometers per hour. They are the fastest trains in China, offering a comfortable travel experience for long-distance trips. - D-series trains
D stands for "Dong Che", which refers to China's bullet trains. These trains run on high-speed rail lines and some conventional rail lines, with speeds reaching up to 250-300 kilometers per hour. The D-series trains provide faster and more comfortable service compared to regular trains. - K-series trains
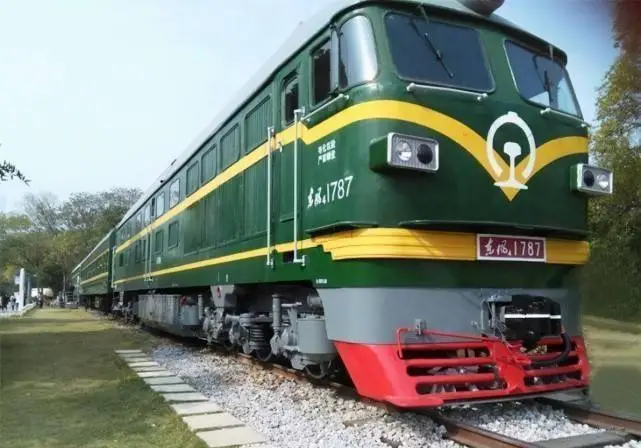
K stands for "Kuai Su", which refers to China's fast-speed trains. They operate on longer routes and have speed and service levels between regular trains and bullet trains. While not as fast as high-speed or bullet trains, K-series trains offer relatively fast service. K-series trains' carriages are green, which is why they are also called "green-skinned trains" (绿皮火车). - C-series trains
C stands for "Cheng Ji" (intercity), which is used for short-distance travel between cities. These trains run on intercity rail lines around cities and are generally faster than regular trains but slower than high-speed trains. They are suitable for quick commutes between cities. - L-series trains
L stands for "Lin Shi" (temporary), which refers to trains that are temporarily added to meet special demands. For example, during peak travel periods like holidays, additional L-series trains may be introduced to accommodate increased passenger volume.



Class Differences
Seat classes on China's railway system are mainly divided into the following categories:
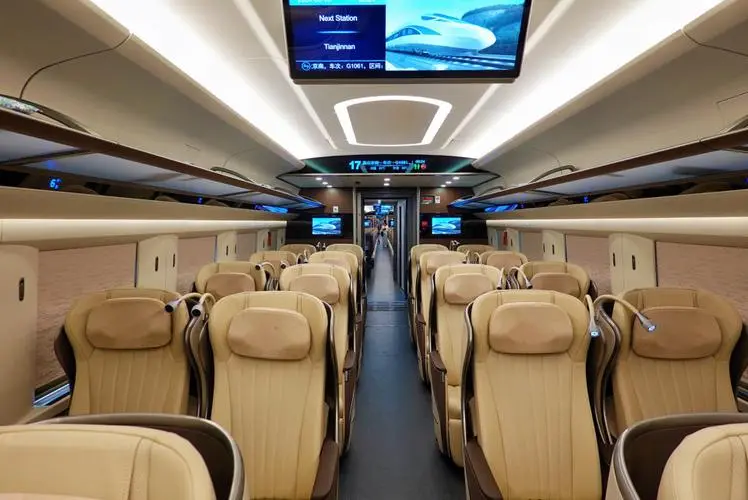
- First Class
Each seat has an individual chair and armrest, with adjustable backrests and leg rests, providing relatively spacious space.
Small tables, power outlets, and complimentary tea are provided.
Typically available on bullet trains (D/G-series trains).

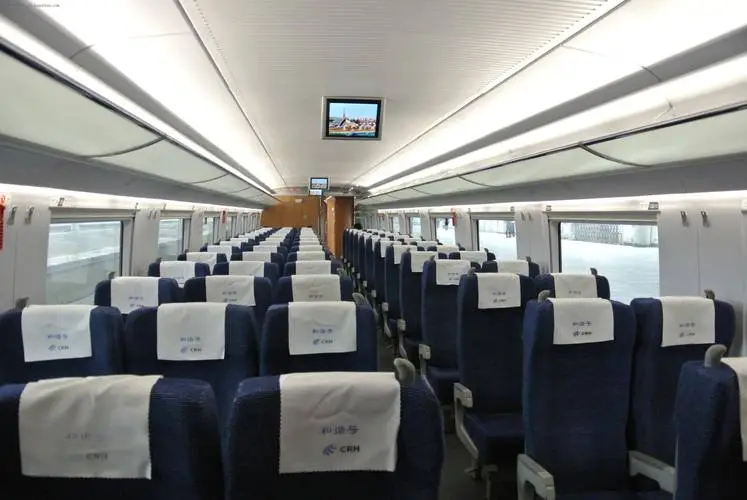
- Second Class
Each seat has an individual chair, but the backrests are not adjustable, and the space is slightly smaller than First Class.
Small tables and power outlets are provided.
The most common seat type on bullet trains (D/G-series trains).

- Standing
No individual seats; passengers stand in the carriage.
Relatively lower prices, usually offered during peak times.
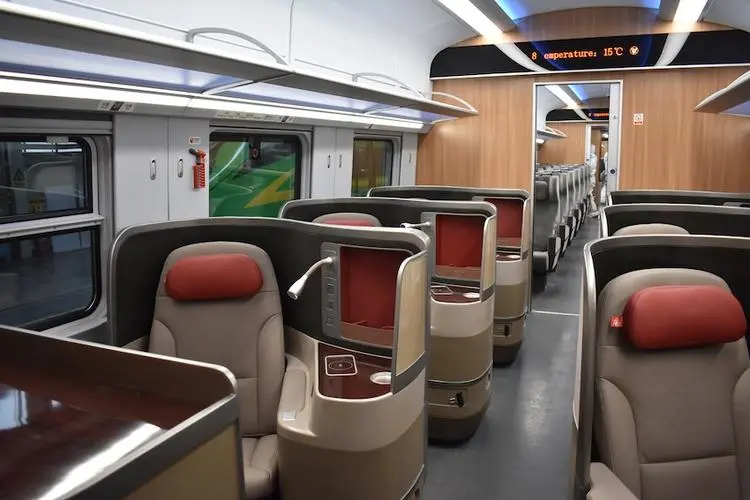
- Business Class
Available on some high-speed trains, usually located in the front carriages.
Each seat is in an individual compartment, offering more space, more comfortable seats, and a wider range of services.
The highest-priced with the best service experience.

- Others
Other types include Special Class, Deluxe Soft Sleeper, Soft Sleeper, Hard Sleeper, Hard Seat, Second Class Sleeper, and Third Class Sleeper. The specific types vary according to the train type and the level of service provided.
Chinese Train Stations
- Major cities have multiple train stations. It's essential to distinguish between North, South, East, and West stations, and remember that directions might be labeled in pinyin, like "dong" (East) or "xi" (West), rather than in English.
Meaning | Chinese pinyin | English phonetic representations | Chinese |
|---|---|---|---|
North | běi | bae | 北 |
South | nán | lamb | 南 |
West | xī | see | 西 |
East | dōng | dumb | 东 |
- Differentiate between high-speed rail stations and regular train stations, as some old stations don’t serve G, C, D trains.
Different trains offer different services and facilities. High-speed trains are modern and comfortable, while normal speed trains may not be so convenient for foreign travelers.
- G, D, and C Trains - Modern Facilities for a Convenient Journey
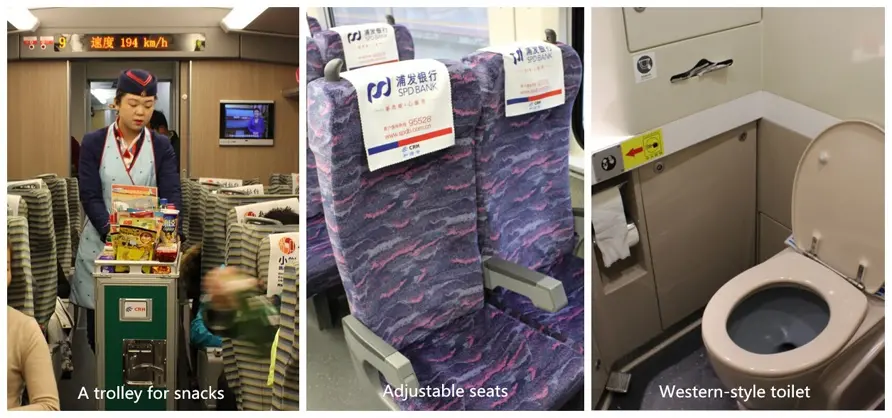

Seating: High-speed trains are fully air-conditioned, and the seats are adjustable for your comfort, similar to airplane seats. Additionally, there is a 220V AC socket under each seat for your devices.
Food: High-speed trains offer various set meals, including options for Muslim food. You can visit the restaurant car for made-to-order meals priced between 20 to 50 yuan per dish. Alternatively, you can purchase a set meal from the attendant's trolley or buy snacks and drinks from the canteen bar.
Toilets: Both Chinese and Western-style toilets, as well as handicapped restrooms, are available between coaches. However, toilets often run out of toilet paper or may not provide it at all.
- Z, K and T Number Only Trains - Not as Comfortable
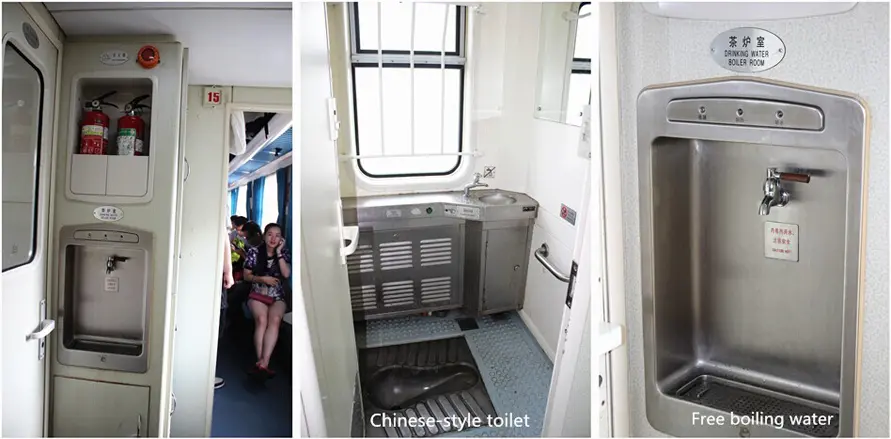

Seating: Hard seats are not adjustable and do not have power outlets. Most normal-speed trains, except for the oldest ones, are fully air-conditioned.
Food: While some trains don't have a restaurant car, most T and K trains do. There is often a staff member who walks through the coaches selling small items, snacks, and drinks from a trolley. We recommend purchasing some simple food and drinks before boarding, such as takeout from KFC or McDonald's, which you can eat at your seat.
Toilets: Most trains only have Chinese-style toilets, which are usually in poor condition. Some soft sleeper and deluxe soft sleeper carriages have Western-style toilets in better condition.
- Unlike other countries, new high-speed rail stations in China are usually located in suburban areas, which is related to China's land policy, which you can explore for more information.
How to Buy Train Tickets
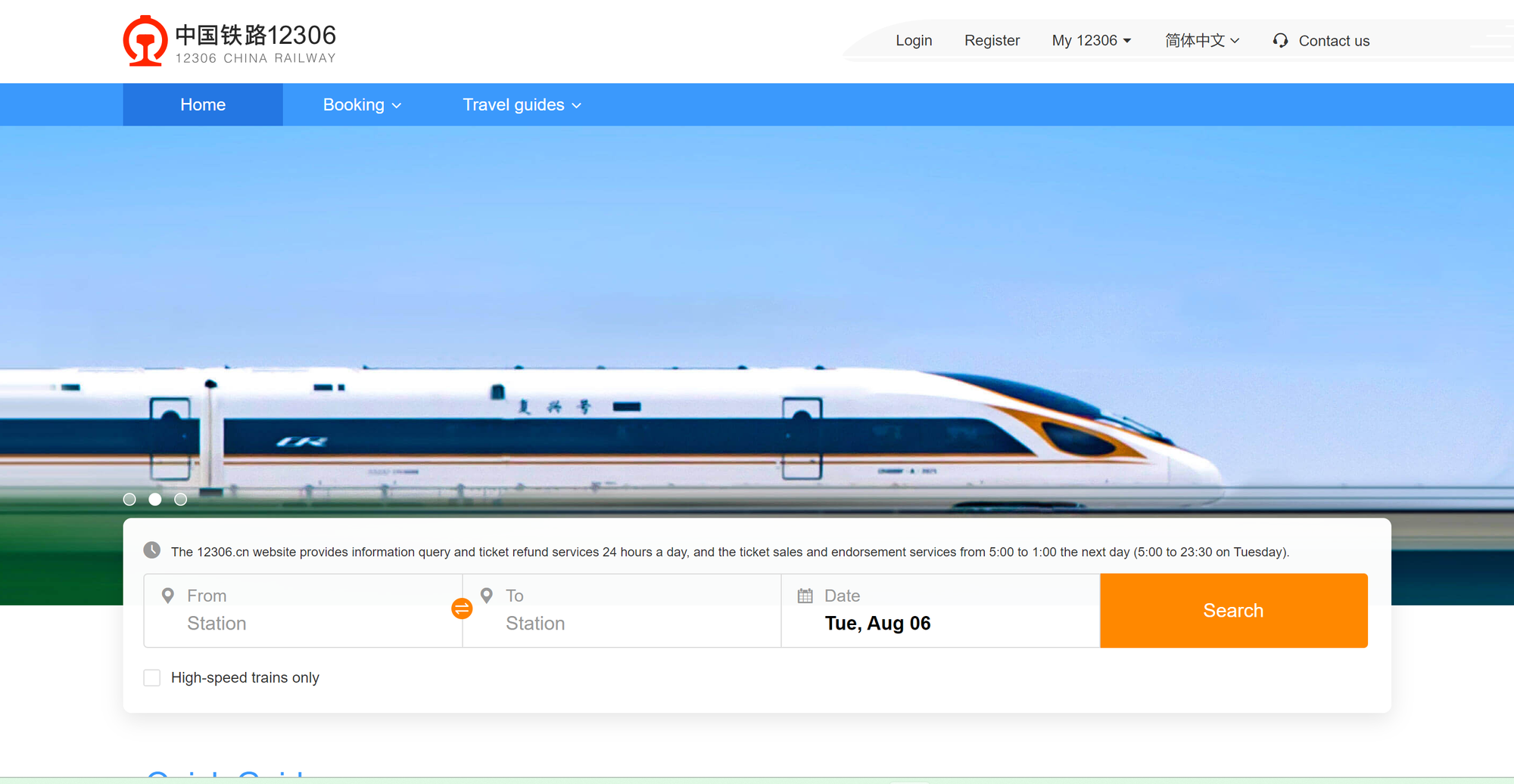
Online via 12306.cn

Official Online Ticket Booking Website
To ensure the safety and order of passenger transportation, railway operation company has implemented real-name ticketing in accordance with related regulations. For the scope of real-name ticketing and the details of ticketing, ID verification and check-in, please refer to station announcements. When purchasing real-name tickets, please show a valid ID document of the passenger. Foreign passengers can purchase real-name tickets with valid passports that can be used according to related regulations.
Ensure you have Alipay or WeChat Pay set up in advance (refer to our [App Usage Guide] for details), enabling you to complete the order and payment within the app.
FAQ about 12306.cn
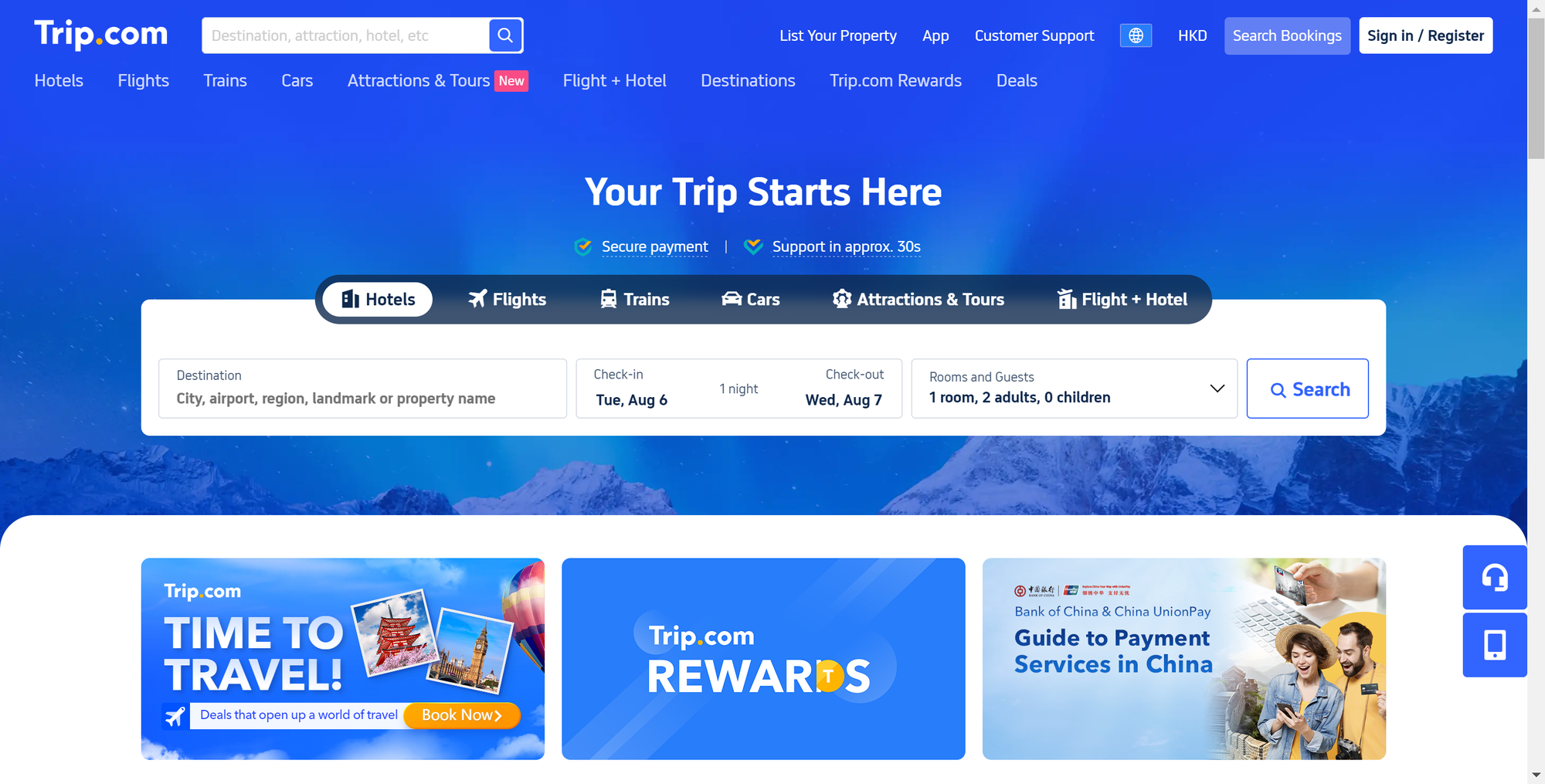
Online via Trip.com

Trip.com is a widely used online ticketing platform that offers a variety of travel-related services, including flight tickets, train tickets, bus tickets, boat tickets, as well as attraction tickets and hotel reservations.
The website is known for its simple user interface and convenient ticketing process, supporting multiple languages including English, providing convenience for international tourists.
Moreover, trip.com also provides an accessible official website, making it easy for users with different needs to use its services. Whether you are planning a short or long trip, trip.com can meet your needs and is a good choice for planning your trip to China.
Offline via Ticket Machines
Some train stations have automatic machines, but due to the popularity of the app, these are less common. Chinese citizens can use their ID cards and mobile payments.
However, it’s not recommended for foreign tourists due to potential compatibility issues with passports.

Offline at Ticket Counters
If you face difficulties online, you can buy tickets at the counter by showing your passport. Show the ticket agent your destination and travel time to choose your options.

How to Travel by Train
Confirm Ticket Purchase Method
If bought via 12306.cn or 12306 app, you won’t have a physical ticket but can check train details on the app.
If bought offline, you'll have a paper ticket. App and website users can also get a paper ticket from machines or counters as a souvenir.
Steps at a High-Speed Rail Station
Entering the Station
No ticket check is needed, just ID verification.
Chinese citizens use ID cards and facial recognition. Foreign visitors with passport chips and facial data recorded upon entry can use machines; otherwise, use manual entry with volunteer assistance.
Security Check
Strict security measures due to past incidents, more thorough than metro checks but less so than airports.
Waiting Area
Find your platform based on ticket or app info. Platforms are labeled with letter-number combinations.
E.g. 16A for platform 16, entrance A.
Boarding
The distances between the ticket office, security check, waiting room, and station platform can be considerable, requiring occasional long walks from one side of the station to the other. While most Chinese passengers no longer need to collect paper tickets, resulting in shorter queues at the ticket office on regular days, it's important to note that during public holidays, the queues can become quite lengthy.
Tickets are checked 10 minutes before departure. Confirm with staff whether to use manual or machine channels.
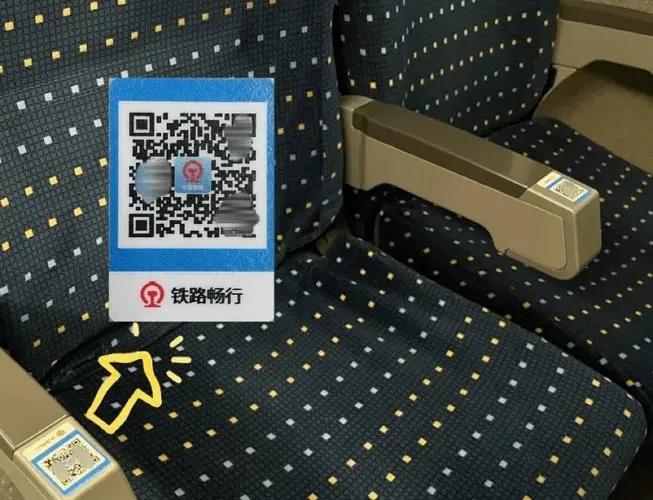
Dining
Meal services available through attendants or via QR code payment on the armrest for delivery.


Restrooms
Maybe squat or seated toilets, located between carriages.
Arrival
Line up in advance to disembark.
Exiting the Station
Options include:
- Metro
- Taxi queue
- Ride-hailing (e.g., Didi) with designated pickup points. For language barriers, use our [online guide service] (see premium services).
Additional Tips
- If in Second Class, ask the passenger behind you before reclining your seat to avoid discomfort and conflict.
- Use headphones and avoid loud conversations or speakerphone calls, as these are considered uncivil behaviors.
- In Second Class, politely communicate with other passengers when needing access to your seat.
- Choose seats beside the window to enjoy the scenery.




